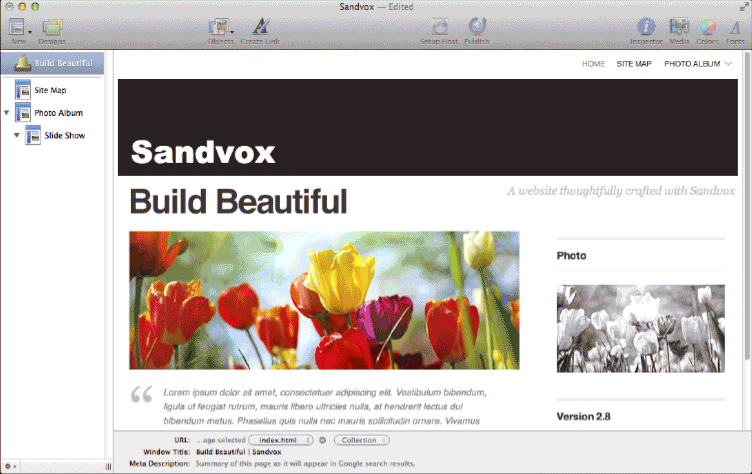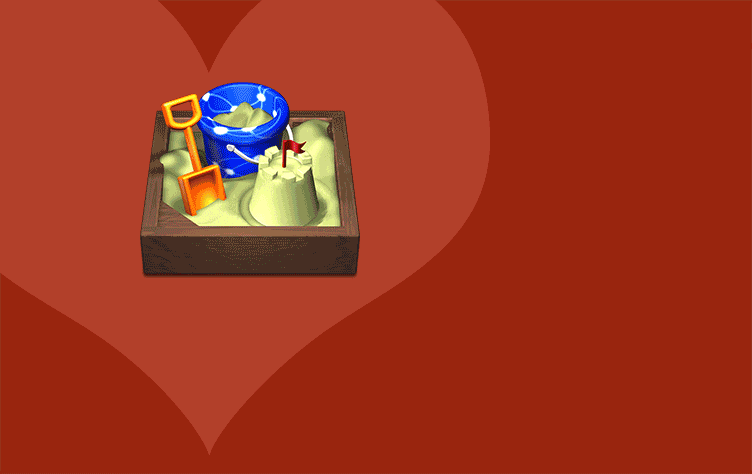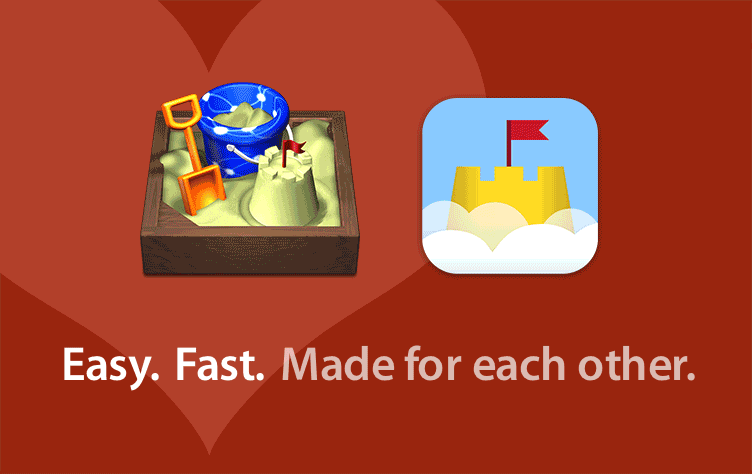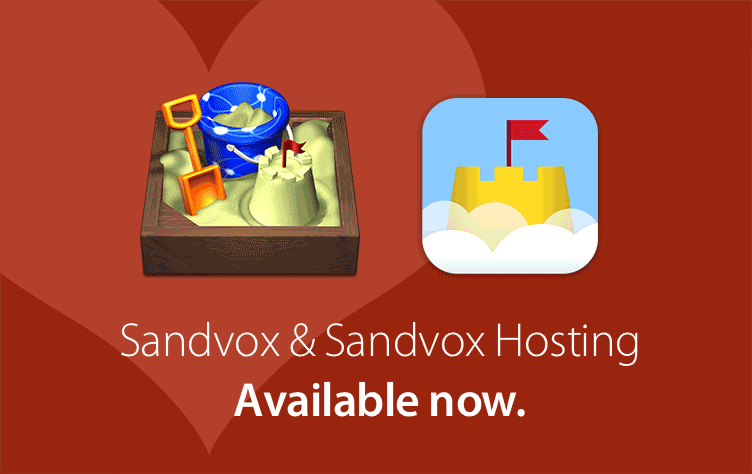
고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
- Pc Maintenance Tool Att
- Itool For Mac
- At&t Pc Maintenance
- Mac System Tools
- Best Free Pc Maintenance Tool
Hello and welcome to my User Tip
The Appalachian Trail is a 2,180+ mile long public footpath that traverses the scenic, wooded, pastoral, wild, and culturally resonant lands of the Appalachian Mountains. Conceived in 1921, built by private citizens, and completed in 1937, today the trail is managed by the National Park Service, US. The latest Tweets from AT&T (@ATT). Connecting you to more of your tweet, tag, retweet, follow thing - that’s our thing.
Although you might have heard that 'Mac's don't need maintenance' they actually do in sense to keep things more or less in line or the machine can become a mess through a users inaction to keep things tidy and updated.
So I'm going to share what you can do to keep your Mac running fine.
Do weekly:
1: Apple Menu > Software Update (repeat until clear) - fixes issues and security problems in Apple provided software.
2: Third Party Software
Open each and search for a update button or visit the developers website and verify the version or uninstall if issues develop according to the developers directions (do no use AppDelete type programs).
A warning flag should go off if your auto-updating program (like Chrome or Firefox) is not the current compatible OS X version. You have a further issue to fix. ..Step by Step to fix your Mac
Check for browser add-ons that if there are any updates for those.
Anti-malware software, update the definitions to make sure it's current.
Note: AppStore software is usually behind about 4-8 weeks. Some developers are not carrying on AppStore anymore so their software might not be current there. Install software directly from the developers website if it's there instead, it will have it's own updater and be faster that way, especially for any software that contacts the Internet routinely, like Opera or other browsers or mail programs.
3: Third Party System Preferences files and Finder menu items - don't forget updating those.
4: Third Party Web Browser Plug-ins - This checker can assist enormously: https://www.mozilla.org/en-US/plugincheck/
5: Reset Safari and all web browsers caches files located in each browser's preferences.
6: Reset Flash and other web browser plugin caches find out where they are located per browser plugin
7: For Privacy. Run the free CCleaner for the Mac: https://www.piriform.com/mac/ccleaner
8: If running another operating system in BootCamp or virtual machine software, revert to a earlier secure snapshot and do all the updates and cleaning.
9: Update your more immediate backup system, either TimeMachine and/or bootable clones if they are disconnected.
10: Do not update your longer term-
-disconnected bootable clone backup until another few weeks have passed to make sure all your software is working as intended, you might have to revert to this earlier machine state to bypass new issues. Most commonly used backup methods
11: Optional scrubbing:
If you have a boot hard drive you can opt to scrub the deleted files off the drive and cure future bad sector issues at the same time by using Disk Utilities > Erase Free Space > Zero option on the Macintosh HD. It will take some time to complete and isnt' necessary, but can assist reduce the possibility of future problems.
Never move a computer or a hard drive while it's running. It's a big cause of many issues on these forums.
SSD's can't be securely erased or scrubbed. How do I securely delete data from the machine?
12: Check for recent security issues:Security Issues Warning List
If your running OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion,
Right click or control click on software that won't run or install that you trust the source of, this will bypass Apple's Gatekeeper and shouldn't be required to do so ever again.
Do monthly:
1: Run the #12/#13 OnyX cache cleaning /repair routine (do not clean the log files, you may need those) and reboot. ..Step by Step to fix your Mac
2: Check your router makers site for firmware updates for your router and apply, they fix security issues. WiFi security issues, at home and WiFi hotspots
3: Update your long term backup/bootable clone if there wasn't a OS X or third party update in the last week or so to make sure it's running as expected.
Do all the time:
1: Don't let your boot hard drive get more than 50% (best performance) or more than 80% filled. Do not ignore the warnings your boot drive is getting filled
2: Don't let your boot Solid State Disk or Flash drive get more than 80% filled. Look in Utilities > Activity Monitor
3: Do not install software or browser plugins from unverifiable sources. Especially if there is no means to get into physical contact with the developer. Security Steps and Behavior
4: Do not visit risky web sites or ignore 'Safe Warnings' as Mac's can also be attacked at malicious web sites. Ideally, use a virtual machine operating system you can purge in a few seconds by reverting to a earlier snapshot. (Linux also can be used and it's free)
5: Do not install software promising to 'speed up your Mac' Learn how your machine works here: Why is my computer slow?
6: Keep a clone backup of each Mac on a powered external drive kept offsite to prevent against fire, theft and acts of man. Most commonly used backup methods
7: Hardening your MacHarden your Mac against malware attacksSecurity Issues Warning List
What you don't need to do:
1: Regular Defragmentation -
Needed only for hard drives (not SSDs) and OS X does it's own so you don't have to unless it's been upgraded or in a very rare long time, then if it's required there is a very safe and long lasting method to go about it here: How to safely defrag a Mac's hard drive
2: Run restrictive or always on anti-virus.
Apple has their own installed and the free ClamXav is good enough for the Windows malware that comes on files in OS X. (but don't affect OS X)
Uninstall the always on anti-virus using the developers uninstall method as it likely installed files into OS X itself, thus needs special uninstaller to remove it.
3: Don't use MacKeeper, it's a burn.
What you should consider having done:
1: Cleaning inside of the machine of dust
One can greatly extend the usable life of their computer if the dust is routinely cleaned out of the machine, especially the cooling fins where it gets clogged at.
Inquire with Apple or Apple Authorized Repair about having the dust cleaned out of the machine at least once a year and determining from that how often to have it done.
Do not open the machine unless it's one of those machines that are user service allowed or you will void your AppleCare/warranty.

Enjoy your Mac. 🙂
Formerly |
|
|---|---|
| Public | |
| Traded as |
|
| ISIN | US00206R1023 |
| Industry | |
| Predecessor | |
| Founded | October 5, 1983; 35 years ago[2] |
| Headquarters | Whitacre Tower, , U.S. |
| Worldwide | |
Key people | Randall L. Stephenson (Chairman and CEO) John Stankey (President and COO) John J. Stephens (SVP and CFO) |
| Products |
|
| Revenue | US$170.756 billion (2018) |
| US$26.096 billion (2018) | |
| US$19.953 billion (2018) | |
| Total assets | US$531 billion (2018) |
| Total equity | US$193.884 billion (2018)[3] |
| 273,210 (2018)[4] | |
| Divisions | |
| Website | about.att.com |
AT&T Inc. is an American multinationalconglomerateholding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas.[5] It is the world's largest telecommunications company, the largest provider of mobile telephone services, and the largest provider of fixed telephone services in the United States through AT&T Communications. Since June 14, 2018, it is also the parent company of mass media conglomerate WarnerMedia, making it the world's largest media and entertainment company in terms of revenue.[6] As of 2018, AT&T is ranked #9 on the Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue.[7]
AT&T Inc. began as the Southwestern Bell Telephone Company, once a subsidiary of the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, or AT&T Corporation, which itself had evolved from the Bell Telephone Company co-founded by Alexander Graham Bell and his father-in-law, Gardiner Greene Hubbard, in 1877.
The 1982 United States v. AT&Tantitrust lawsuit resulted in the divestiture of AT&T Corporation's ('Ma Bell's) subsidiaries or Regional Bell Operating Companies (RBOCs), commonly referred to as 'Baby Bells', resulting in several independent companies, including Southwestern Bell Corporation; the latter changed its name to SBC Communications Inc. in 1995.
In 2005, SBC purchased its former parent AT&T Corporation and took on its branding, with the merged entity naming itself AT&T Inc. and using its iconic logo and stock-trading symbol. In 2006, AT&T Inc. acquired BellSouth, the last independent Baby Bell company, making their formerly joint venture Cingular Wireless (which had acquired AT&T Wireless in 2004) wholly owned and rebranding it as AT&T Mobility.
The current AT&T reconstitutes much of the former Bell System, and includes ten of the original 22 Bell Operating Companies along with the original long distance division.[8]
- 1History
- 2AT&T Latin America
- 3Landline operating companies
- 4Corporate structure
- 7Criticism and controversies
- 8Naming rights and sponsorships
History[edit]
Origin and growth (1885–1981)[edit]
AT&T can trace its origin back to the Bell Telephone Company founded by Alexander Graham Bell, Gardiner Greene Hubbard, and Thomas Sanders after Bell’s patenting of the telephone.[9] One of that company's subsidiaries was American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), established in 1885,[10] which acquired the Bell Company on December 31, 1899, for legal reasons, leaving AT&T as the main company. AT&T established a network of subsidiaries in the United States and Canada that held a phone service monopoly, authorized by government authorities with the Kingsbury Commitment, throughout most of the twentieth century. This monopoly was known as the Bell System,[11] and during this period, AT&T was also known by the nickname Ma Bell.[12] For periods of time, the former AT&T was the world's largest phone company.
Breakup and reformation (1982–2004)[edit]
In 1982, U.S. regulators broke up the AT&T monopoly, requiring AT&T to divest its regional subsidiaries and turning them each into individual companies. These new companies were known as Regional Bell Operating Companies, or more informally, Baby Bells.[13] AT&T continued to operate long distance services, but as a result of this breakup, faced competition from new competitors such as MCI and Sprint.
Southwestern Bell was one of the companies created by the breakup of AT&T Corp. The architect of divestiture for Southwestern Bell was Robert G. Pope. The company soon started a series of acquisitions. This includes the 1987 acquisition of Metromedia mobile business and the acquisition of several cable companies in the early 1990s. In the later half of the 1990s, the company acquired several other telecommunications companies, including some Baby Bells, while selling its cable business. During this time, the company changed its name to SBC Communications. By 1998, the company was in the top 15 of the Fortune 500, and by 1999 the company was part of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (lasting through 2015).
Purchase of former parent and acquisitions (2005–2014)[edit]
In 2005, SBC purchased AT&T for $16 billion. After this purchase, SBC adopted the better-known AT&T name and brand, with the original AT&T Corp. still existing as the long-distance landline subsidiary of the merged company. The current AT&T claims the original AT&T Corp.'s history (dating to 1885) as its own. However, it retains SBC's 1983-2005 corporate structure.[14] It also retains SBC's pre-2005 stock price history, and all regulatory filings prior to 2005 are for Southwestern Bell/SBC, not AT&T Corp.
In September 2013, AT&T Inc. announced it would expand into Latin America through a collaboration with América Móvil.[15] In December 2013, AT&T announced plans to sell its Connecticut wireline operations to Stamford-based Frontier Communications.[16]
Recent developments (2014–present)[edit]
AT&T purchased the Mexican carrier Iusacell in late 2014,[17] and two months later purchased the Mexican wireless business of NII Holdings,[18] merging the two companies to create AT&T Mexico.
In July 2015, AT&T purchased DirecTV for $48.5 billion, or $67.1 billion including assumed debt,[19] subject to certain conditions.[20][21] AT&T subsequently announced plans to converge its existing U-verse home internet and IPTV brands with DirecTV, to create AT&T Entertainment.[22][23][24]
On October 22, 2016, AT&T announced a deal to buy Time Warner for $108.7 billion in an effort to increase its media holdings.[25][26][27][28][29][30]
AT&T also owns approximately a 2% stake in Canadian-domiciled entertainment company Lionsgate.[31]
On July 13, 2017, it was reported that AT&T would introduce a cloud-basedDVR streaming service as part of its effort to create a unified platform across DirecTV and its DirecTV Now streaming service, with U-verse to be added soon.[32][33][34] In October 2018, it was announced that the service would launch in 2019.[35][36] Named HBO Max, the service's release date was pushed to 2020.[37]
On September 12, 2017, it was reported that AT&T planned to launch a new cable TV-like service for delivery over-the-top over its own or a competitor's broadband network sometime next year.[38]

On November 20, 2017, Assistant Attorney General Makan Delrahim filed a lawsuit for the United States Department of Justice Antitrust Division to block the merger with Time Warner, saying it 'will harm competition, result in higher bills for consumers and less innovation.'[39][40] In order for AT&T to fully acquire Time Warner, the Department of Justice stated that the company must divest either DirecTV or Turner Broadcasting System.[41]
As of 2017, AT&T is the world's largest telecommunications company.[42] AT&T is also the second largest provider of mobile telephone services and the largest provider of fixed telephone services in the United States.[43]
On March 7, 2018, the company prepared to sell a minority stake of DirecTV Latin America through an IPO, creating a new holding company for those assets named Vrio Corp.[44][45] However, on April 18, 2018, just a day before the public debut of Vrio, AT&T canceled the IPO due to market conditions.[46][47]
On June 12, 2018, AT&T was given permission by U.S. District Court Judge Richard J. Leon to go ahead with its $85 billion deal for Time Warner. The DOJ had attempted to stop the merger fearing it would harm competition.[48] The merger closed two days after, becoming a wholly owned subsidiary and division of AT&T with a new name, WarnerMedia, announced the next day.[49]
Three months after completing the acquisition, AT&T reorganized into four main units: Communications, including consumer and business wireline telephony, AT&T Mobility, and consumer entertainment video services; WarnerMedia, including Turner cable television networks, Warner Bros. film and television production, and HBO; AT&T Latin America, consisting of wireless service in Mexico and video in Latin America and the Caribbean under the Vrio brand; and Advertising and Analytics, since renamed Xandr.[50][51]
AT&T Latin America[edit]
Formerly | AT&T International, Inc. (2017-2018) |
|---|---|
| Division | |
| Industry | Telecommunication |
| Founded | 2017; 2 years ago |
| Headquarters | Dallas, Texas , |
Area served | Mexico |
Key people | Lori Lee (CEO) |
| Products | Wireless Satellite television |
| Revenue | US$7 billion (2018)[53] |
| Parent | AT&T |
| Subsidiaries | AT&T Mexico Vrio |
| Website | www.att.com |
AT&T Latin America (formerly AT&T International, Inc.) is a wholly owned division of AT&T which operates in Mexico and 11 countries in South America.[54]
History[edit]
In 2017, AT&T announced a new AT&T International corporate division housing AT&T Mexico, DirecTV Latin America and their stakes of SKY Brazil and Sky Mexico.[55]
In October 2016, AT&T announced a deal to acquire Time Warner worth $85.4 billion (including assumed Time Warner debt). The proposed deal would give AT&T significant holdings in the media industry; AT&T's competitor Comcast had previously acquired NBCUniversal in a similar bid to increase its media holdings, in concert with its ownership of television and internet providers. If approved by federal regulators, the merger would bring Time Warner's properties under the same umbrella as AT&T's telecommunication holdings, including satellite provider DirecTV.[56][57][58]
By the end of July, the company announced that, effective August 1, a new structure was created before the acquisition would close. On September 15, 2017, Reuters reported, citing anonymous sources, that AT&T, the owner of DIRECTV's U.S. and Latin American divisions, had hired an advisor to consider offering AT&T Latin America on the public stock market. In November 2017, the U.S. Justice Department said it was moving to sue to block the AT&T-Time Warner merger.[59] On November 20, 2017, the Department of Justice filed an antitrust lawsuit over the acquisition; Makan Delrahim stated that the deal would 'greatly harm American consumers'. AT&T asserts that this suit is a 'radical and inexplicable departure from decades of antitrust precedent'.[60] On December 22, 2017, the merger agreement deadline was extended to June 21, 2018.[61] On April 19, 2018, the IPO was cancelled. On June 12, 2018, the AT&T-Time Warner merger was approved by a federal judge.[62] Two days later, AT&T completed the acquisition of Time Warner, and a day later the company was renamed WarnerMedia.
On September 21, 2018, AT&T reclassified it four principal divisions which includes AT&T International which now have some assets moved out like the RSNs, an also merging Consumer Mobility, Technology and Business Mobility and renamed the company as AT&T Latin America.[50]
Landline operating companies[edit]
Of the eight companies that were part of the Breakup of the Bell System, these five are a part of the current AT&T:[63]
- Ameritech, acquired by SBC in 1999
- AT&T Corp., acquired by SBC in 2005
- BellSouth, acquired by AT&T in 2006
- Pacific Telesis, acquired by SBC in 1997
- Southwestern Bell, rebranded as SBC Communications in 1995
Chart of Baby Bells[edit]
| AT&T Corporation RBOCs grouped into 'Baby Bells' split off in 1984 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BellSouth | AT&T Corp. (non-LEC) | Ameritech | Pacific Telesis | Southwestern Bell Corp. (later SBC Communications) | Bell Atlantic | NYNEX | US West | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GTE Corporation (non-RBOCILEC) | Qwest(non-ILEC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Verizon | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AT&T Inc. (former SBC) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CenturyLink (non-RBOCILEC) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AT&T Inc. | Verizon | CenturyLink |
Former operating companies[edit]
The following companies have become defunct or were sold under SBC/AT&T ownership:
- Southern New England Telephone: sold to Frontier Communications in 2014[64]
- Woodbury Telephone: merged into Southern New England Telephone on June 1, 2007.[65]
Future of rural landlines[edit]
AT&T stated that it would declare the intentions for its rural landlines on November 7, 2012.[66] AT&T had previously announced that it was considering a sale of its rural landlines, which are not wired for AT&T's U-verse service; however, it has also stated that it may keep the business after all.[needs update]
AT&T was not the first Baby Bell to sell off rural landlines. Ameritech sold some of its Wisconsin lines to CenturyTel in 1998; BellSouth sold some of its lines to MebTel in the 2000s; U S WEST sold many historically Bell landlines to Lynch Communications and Pacific Telecom in the 1990s; Verizon sold many of its New England lines to FairPoint in 2008 and its West Virginia operations to Frontier Communications in 2010.
On October 25, 2014, Frontier Communications took over control of the AT&T landline network in Connecticut after being approved by state utility regulators. The deal was worth about $2 billion, and included Frontier inheriting about 2,500 of AT&T's employees and many of AT&T's buildings.[67]
Corporate structure[edit]
Facilities and regions[edit]
The company is headquartered at Whitacre Tower in downtown Dallas, Texas.[5] On June 27, 2008, AT&T announced that it would move its corporate headquarters from downtown San Antonio to One AT&T Plaza in downtown Dallas.[5][68] The company said that it moved to gain better access to its customers and operations throughout the world, and to the key technology partners, suppliers, innovation and human resources needed as it continues to grow, domestically and internationally.[69] AT&T Inc. previously relocated its corporate headquarters to San Antonio from St. Louis, Missouri, in 1992, when it was then named Southwestern Bell Corporation. The company's Telecom Operations group, which serves residential and regional business customers in 22 U.S. states, remains in San Antonio.[citation needed] Atlanta, Georgia, continues to be the headquarters for AT&T Mobility, with significant offices in Redmond, Washington, the former home of AT&T Wireless. Bedminster, New Jersey, is the headquarters for the company's Global Business Services group and AT&T Labs, and is where the original AT&T Corp. remains located. St. Louis continues as home to the company's Directory operations, AT&T Advertising Solutions.[70]
AT&T offers also services in many locations throughout the Asia Pacific; its regional headquarters is located in Hong Kong.[71] The company is also active in Mexico, and it was announced on November 7, 2014, that Mexican carrier Iusacell is being acquired by AT&T.[17] The acquisition was approved in January 2015.[citation needed][72][73] On April 30, 2015, AT&T acquired wireless operations Nextel Mexico from NII Holdings (now AT&T Mexico).[74]
Corporate governance[edit]
AT&T's current board of directors as of May 2019:[75]
- Randall L. Stephenson – chairman
- Cynthia B. Taylor
- Geoffrey Y. Yang[75]
The current management as of October 2019 includes:[76]
- Randall L. Stephenson – chief executive officer (CEO)
- Angela Santone- chief administrative officer (CAO)
- William A. Blase, Jr. – senior executive vice president of human resources
- John J. Stephens – senior executive vice president and chief financial officer (CFO)
- David S. Huntley – senior executive vice president and chief compliance officer
- David R. McAtee II – senior executive vice president and general counsel
- Lori Lee – CEO of AT&T Latin America and global marketing officer
- John Stankey – President and COO of AT&T Inc., CEO of WarnerMedia
Political involvement[edit]
According to the Center for Responsive Politics, as of 2018, AT&T is the fifteenth-largest donor to United States political campaigns,[77] and was the top American corporate donor in 2011,[78] having contributed more than US$47.7 million since 1990, 56% of which went to Republicans and 44% of which went to Democrats.[79] As an example, in 2005, AT&T was among 53 entities that contributed the maximum of $250,000 to the second inauguration of President George W. Bush.[80][81][82] Bill Leahy, representing AT&T, sits on the Private Enterprise Board of the American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC).[83] ALEC is a nonprofit organization of conservativestate legislators and private sector representatives that drafts and shares model state-level legislation for distribution among state governments in the United States.[84][85][86]
During the period of 1998 to 2010, the company expended US$130 million on lobbying in the United States.[78] A key political issue for AT&T has been the question of which businesses win the right to profit by providing broadband internet access in the United States.[87] The company has also lobbied in support of several federal bills. AT&T supported the Federal Communications Commission Process Reform Act of 2013 (H.R. 3675; 113th Congress), a bill that would make a number of changes to procedures that the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) follows in its rulemaking processes.[88] The FCC would have to act in a more transparent way as a result of this bill, forced to accept public input about regulations.[89] AT&T's Executive Vice President of Federal Relations, Tim McKone, said that the bill's 'much needed institutional reforms will help arm the agency with the tools to keep pace with the Internet speed of today's marketplace. It will also ensure that outmoded regulatory practices for today's competitive marketplace are properly placed in the dustbin of history.'[90]
In May 2018, reports emerged that AT&T made 12 monthly payments between January and December 2017 to Essential Consultants, a company set up by President Donald Trump's lawyer Michael Cohen, totaling $600,000.[91] Although initial reports on May 8 mentioned only four monthly payments totaling $200,000,[92] documents obtained by The Washington Post on May 10 confirmed the figure of 12 payments, which had begun three days after the President was sworn into office.[93][94] AT&T confirmed the report the same day.[95] The report from The Washington Post, as well as additional reporting from Bloomberg, revealed the payments had been made for Cohen to 'provide guidance' relating to the attempted $85 billion merger with Time Warner,[93][94] to gain information on the Trump administration's planned tax reforms, as well as about potential changes to net neutrality policies under the new FCC.[96] However, Chairman of the FCC Ajit Pai denied Cohen ever inquired about net neutrality on AT&T's behalf.[95][97] A spokesperson for AT&T said that the company had been contacted by the Special Counsel investigation led by Robert Mueller regarding the payments, and had provided all the information requested in November and December 2017.[98][99]
In early 2019 the Democratic House Judiciary requested records related to the AT&T-Time Warner merger from the White House.[100]
Historical financial performance[edit]
The financial performance of the company is reported to shareholders on an annual basis and a matter of public record. The unit (except where noted) is billions of US dollars. Where performance has been restated, the most recent statement of performance from an annual report is used.[101][102][103][104]
| Year | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | 45.38 | 42.82 | 40.50 | 40.79 | 43.86 | 63.06 | 118.9 | 124.0 | 122.5 | 124.8 | 126.7 | 127.4 | 128.8 | 132.4 | 146.8 | 163.8 |
| Net Income | 7.008 | 5.653 | 8.505 | 5.887 | 4.768 | 7.356 | 11.95 | 12.87 | 12.12 | 19.09 | 3.944 | 7.264 | 18.25 | 6.224 | 13.69 | 13.33 |
| Assets | 96.42 | 95.17 | 102.0 | 110.3 | 145.6 | 270.6 | 275.6 | 265.2 | 268.3 | 268.5 | 270.3 | 272.3 | 277.8 | 292.8 | 402.7 | 403.8 |
| Number of employees (thousands) | 193.4 | 175.0 | 168.0 | 162.7 | 190.0 | 304.2 | 309.1 | 302.7 | 282.7 | 266.6 | 256.4 | 241.8 | 243.4 | 243.6 | 281.5 | 268.5 |
Criticism and controversies[edit]
Pc Maintenance Tool Att
Hemisphere database[edit]
The company maintains a database of call detail records of all telephone calls that have passed through its network since 1987. AT&T employees work at High Intensity Drug Trafficking Area offices (operated by the Office of National Drug Control Policy) in Los Angeles, Atlanta, and Houston so data can be quickly turned over to law enforcement agencies. Records are requested via administrative subpoena, without the involvement of a court or grand jury.
Censorship[edit]
In September 2007, AT&T changed its legal policy to state that 'AT&T may immediately terminate or suspend all or a portion of your Service,[105] any Member ID, electronic mail address, IP address, Universal Resource Locator or domain name used by you, without notice for conduct that AT&T believes ... (c) tends to damage the name or reputation of AT&T, or its parents, affiliates and subsidiaries.'[106] By October 10, 2007, AT&T had altered the terms and conditions for its Internet service to explicitly support freedom of expression by its subscribers, after an outcry claiming the company had given itself the right to censor its subscribers' transmissions.[107] Section 5.1 of AT&T's new terms of service now reads 'AT&T respects freedom of expression and believes it is a foundation of our free society to express differing points of view. AT&T will not terminate, disconnect or suspend service because of the views you or we express on public policy matters, political issues or political campaigns.'[108]
Privacy controversy[edit]
In 2006, the Electronic Frontier Foundation lodged a class action lawsuit, Hepting v. AT&T, which alleged that AT&T had allowed agents of the National Security Agency (NSA) to monitor phone and Internet communications of AT&T customers without warrants. If true, this would violate the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act of 1978 and the First and Fourth Amendments of the U.S. Constitution. AT&T has yet to confirm or deny that monitoring by the NSA is occurring. In April 2006, a retired former AT&T technician, Mark Klein, lodged an affidavit supporting this allegation.[110][111] The Department of Justice has stated it will intervene in this lawsuit by means of State Secrets Privilege.[112]
In July 2006, the United States District Court for the Northern District of California – in which the suit was filed – rejected a federal government motion to dismiss the case. The motion to dismiss, which invoked the State Secrets Privilege, had argued that any court review of the alleged partnership between the federal government and AT&T would harm national security. The case was immediately appealed to the Ninth Circuit. It was dismissed on June 3, 2009, citing retroactive legislation in the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act.[citation needed][113]
In May 2006, USA Today reported that all international and domestic calling records had been handed over to the National Security Agency by AT&T, Verizon, SBC, and BellSouth for the purpose of creating a massive calling database.[114] The portions of the new AT&T that had been part of SBC Communications before November 18, 2005, were not mentioned.
On June 21, 2006, the San Francisco Chronicle reported that AT&T had rewritten rules on its privacy policy. The policy, which took effect June 23, 2006, says that 'AT&T – not customers – owns customers' confidential info and can use it 'to protect its legitimate business interests, safeguard others, or respond to legal process.'[115]
On August 22, 2007, National Intelligence Director Mike McConnell confirmed that AT&T was one of the telecommunications companies that assisted with the government's warrantless wire-tapping program on calls between foreign and domestic sources.[116]
On November 8, 2007, Mark Klein, a former AT&T technician, told Keith Olbermann of MSNBC that all Internet traffic passing over AT&T lines was copied into a locked room at the company's San Francisco office – to which only employees with National Security Agency clearance had access.[117]
AT&T keeps for five to seven years a record of who text messages whom and the date and time, but not the content of the messages.[118]
AT&T has a one star privacy rating from the Electronic Frontier Foundation.[119]
Intellectual property filtering[edit]
In January 2008, the company reported plans to begin filtering all Internet traffic which passes through its network for intellectual property violations.[120] Commentators in the media have speculated that if this plan is implemented, it would lead to a mass exodus of subscribers leaving AT&T,[121] although this is misleading as Internet traffic may go through the company's network anyway.[120] Internet freedom proponents used these developments as justification for government-mandated network neutrality.
Discrimination against local Public-access television channels[edit]
AT&T is accused by community media groups of discriminating against local Public, educational, and government access (PEG) cable TV channels, by 'impictions that will severely restrict the audience'.[122]
According to Barbara Popovic, Executive Director of the Chicago public-access service CAN-TV, the new AT&T U-verse system forces all Public-access television into a special menu system, denying normal functionality such as channel numbers, access to the standard program guide, and DVR recording.[122] The Ratepayer Advocates division of the California Public Utilities Commission reported: 'Instead of putting the stations on individual channels, AT&T has bundled community stations into a generic channel that can only be navigated through a complex and lengthy process.'[122]
Sue Buske (president of telecommunications consulting firm the Buske Group and a former head of the National Federation of Local Cable Programmers/Alliance for Community Media) argue that this is 'an overall attack [...] on public access across the [United States], the place in the dial around cities and communities where people can make their own media in their own communities'.[122]
Itool For Mac
Information security[edit]
In June 2010, a hacker group known as Goatse Security discovered a vulnerability within AT&T that could allow anyone to uncover email addresses belonging to customers of AT&T 3G service for the AppleiPad.[123] These email addresses could be accessed without a protective password.[124] Using a script, Goatse Security collected thousands of email addresses from AT&T.[123] Goatse Security informed AT&T about the security flaw through a third party.[125] Goatse Security then disclosed around 114,000 of these emails to Gawker Media, which published an article about the security flaw and disclosure in Valleywag.[123][125] Praetorian Security Group criticized the web application that Goatse Security exploited as 'poorly designed'.[123]
In April 2015, AT&T was fined $25 million over data security breaches, marking the largest ever fine issued by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for breaking data privacy laws. The investigation revealed the theft of details of approximately 280,000 people from call centres in Mexico, Colombia and the Philippines.[126][127]
Accusations of enabling fraud[edit]
In March 2012, the United States federal government announced a lawsuit against AT&T. The specific accusations state that AT&T 'violated the False Claims Act by facilitating and seeking federal payment for IP Relay calls by international callers who were ineligible for the service and sought to use it for fraudulent purposes. The complaint alleges that, out of fears that fraudulent call volume would drop after the registration deadline, AT&T knowingly adopted a non-compliant registration system that did not verify whether the user was located within the United States. The complaint further contends that AT&T continued to employ this system even with the knowledge that it facilitated use of IP Relay by fraudulent foreign callers, which accounted for up to 95 percent of AT&T's call volume. The government's complaint alleges that AT&T improperly billed the TRS Fund for reimbursement of these calls and received millions of dollars in federal payments as a result.'[128]
Racism[edit]
On April 28, 2015, AT&T announced that it had fired Aaron Slator, President of Content and Advertising Sales, for sending racist text messages.[129] Slator was also hit with a $100 million discrimination lawsuit, filed by African-American employee Knoyme King.[130] The day before that, protesters arrived at AT&T's headquarters in Dallas and its satellite offices in Los Angeles as well as at the home of CEO Randall Stephenson to protest alleged systemic racial policies. According to accounts, the protesters are demanding AT&T begin working with 100% black-owned media companies.[131]
Trademark violation[edit]
In June 2016, Citigroup sued AT&T for trademark infringement, false designation of origin, and unfair competition. The company had recently established a loyalty program under the brand AT&T Thanks, which Citigroup claims would cause consumer confusion as an infringement of its 'ThankYou' and 'Citi ThankYou' marks due to similar wording and visual design. Citi, which also provides a co-branded credit card for AT&T that links with its ThankYou rewards program, sought unspecified damages and the expungement of AT&T's trademark registration.[132][133]
The suit was dismissed in August 2016, with a judge ruling that there was a low likelihood of confusion between the two marks because the companies fall within different industries, and that consumers who use loyalty programs would be able to 'clearly take into account the attributes associated with the products they purchase' and, thus, be able to distinguish them.[134]
Naming rights and sponsorships[edit]
Buildings[edit]
- Whitacre Tower (One AT&T Plaza) – Corporate Headquarters, Dallas, Texas
- AT&T 220 Building – building in Indianapolis, Indiana
- AT&T Building – building in Detroit, Michigan
- AT&T Building – building in Indianapolis, Indiana
- AT&T Building – building in Kingman, Arizona
- AT&T Building – (aka 'The Batman Building') in Nashville, Tennessee
- AT&T Building – building in Omaha, Nebraska
- AT&T Building Addition – building in Detroit, Michigan
- AT&T Building – building in San Diego
- AT&T Center – building in Los Angeles
- AT&T Center – building in St. Louis, Missouri
- AT&T City Center – building in Birmingham, Alabama
- AT&T Corporate Center – building in Chicago, Illinois
- AT&T Huron Road Building – building in Cleveland, Ohio
- AT&T Lenox Park Campus – AT&T Mobility Headquarters in DeKalb County just outside Atlanta, Georgia
- AT&T Midtown Center – building in Atlanta, Georgia
- AT&T Switching Center – building in Los Angeles
- AT&T Switching Center – building in Oakland, California
- AT&T Switching Center – building in San Francisco
- AT&T Tower - building in Minneapolis, MN
- AT&T Building - building in (Meriden), CT
- AT&T Entertainment Group HQ - DirecTV corporate campus in El Segundo, California
Venues[edit]
- AT&T Center – San Antonio, Texas (formerly SBC Center)
- AT&T Field – Chattanooga, Tennessee (formerly BellSouth Park)
- AT&T Plaza – Chicago, Illinois (public space that hosts the Cloud Gate sculpture in Millennium Park)
- AT&T Plaza – Dallas, Texas (plaza in front of the American Airlines Center at Victory Park)
- AT&T Performing Arts Center – Dallas, Texas
- AT&T Stadium – Arlington, Texas (formerly Dallas Cowboys Stadium)
- Jones AT&T Stadium – Lubbock, Texas (formerly Clifford B. and Audrey Jones Stadium, Jones SBC Stadium)
- TPC San Antonio – San Antonio, Texas (AT&T Oaks Course & AT&T Canyons Course)
- War Memorial Stadium, AT&T Field - Little Rock, Arkansas
Sponsorships[edit]
- AT&T Byron Nelson - Irving, Texas (golf)
- AT&T Cotton Bowl Classic (formerly Mobil Cotton Bowl Classic, Southwestern Bell Cotton Bowl Classic, SBC Cotton Bowl Classic) – played in Arlington, Texas, at AT&T Stadium (football)
- AT&T National – Washington, D.C. (golf)
- AT&T Pebble Beach National Pro-Am (golf)
- AT&T Red River Rivalry – Dallas, Texas (formerly Red River Shootout, SBC Red River Rivalry) (football)
- Major League Soccer and the United States Soccer Federation, including the U.S. men's and U.S. women's national teams and the Major League Soccer All-Star Game from 2009
- United States Olympic team[135]
- National Collegiate Athletic Association (Corporate Champion)[136]
- AT&T American Cup, artistic gymnastics competition. Sponsored by AT&T since 2011.
- Red Bull Racing (Formula 1 racing team), technical support and sponsorship, since 2011.[137]
- Cloud9, sponsorship since March 2019.[138][139]
See also[edit]
- Bell System
- Bell System Divestiture
- NSA warrantless surveillance
References[edit]
- ^Form 8-K. Securities and Exchange Commission. October 25, 2004. Accessed January 16, 2019.
- ^Restated Certificate of Incorporation of AT&T Inc.Securities and Exchange Commission. April 24, 2009. Accessed September 3, 2017.
- ^'2018 AT&T Earnings Investor Briefing'(PDF). AT&T. January 30, 2019.
- ^'AT&T Inc. 2018 Quarterly Report (10-Q)'. U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. August 2, 2018. Retrieved September 4, 2018.
- ^ abcGodinez, Victor and David McLemore. 'AT&T moving headquarters to Dallas from San Antonio.' The Dallas Morning News. Saturday June 28, 2008. Retrieved June 18, 2009.
- ^'Bloomberg - Are you a robot?'. www.bloomberg.com.
- ^'Fortune 500 Companies 2018: Who Made the List'. Fortune. Retrieved November 9, 2018.
- ^Kleinfield, Sony (1981). The biggest company on earth: a profile of AT&T. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston. ISBN978-0-03-045326-7.
- ^'Home| History| AT&T'. www.corp.att.com. Retrieved March 3, 2017.
- ^'History of the AT&T Network — Milestones in AT&T Network History| History| AT&T'. www.corp.att.com. Retrieved April 21, 2017.
- ^Pollack, Andrew (January 1, 1984). 'BELL SYSTEM BREAKUP OPENS ERA OF GREAT EXPECTATIONS AND GREAT CONCERN'. The New York Times. ISSN0362-4331. Retrieved May 24, 2017.
- ^Pagliery, Jose (May 20, 2014). 'How AT&T got busted up and pieced back together'. CNNMoney. Retrieved May 24, 2017.
- ^'Lessons from the AT&T break up, 30 years later-CICTP'. Tech Policy Daily. January 3, 2014. Archived from the original on April 22, 2017. Retrieved April 21, 2017.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|dead-url=(help) - ^'AT&T Tech Channel'. Youtube.
- ^Sinead Carew (September 18, 2013). 'AT&T to expand in Latin America with America Movil deal'. Reuters.
- ^AT&T (December 17, 2013). 'AT&T Announces Plans to Sell Connecticut Wireline Operations to Frontier Communications for $2.0 Billion'. AT&T.
- ^ abNguyen, Chuong (November 7, 2014). 'AT&T to expand North American coverage area with Mexico carrier Iusacell acquisition'. Android Central. Retrieved January 1, 2016.
- ^'AT&T to buy NII Holdings' wireless business in Mexico'. Reuters. January 26, 2015. Retrieved January 1, 2016.
- ^'AT&T Completes Acquisition of DirecTV'. Reuters. January 26, 2015. Retrieved January 1, 2016.
- ^'AT&T & DirecTV Merger Gets FCC Approval – With Conditions'. Deadline Hollywood. July 24, 2015. Retrieved July 24, 2015.
- ^'FCC approves AT&T–DirecTV merger'. The Verge. Vox Media. July 24, 2015. Retrieved July 24, 2015.
- ^Bode, Karl (December 2, 2015). 'AT&T Plans on Killing the DirecTV Name Starting in January'. DSL Reports. Retrieved December 2, 2015.
- ^Farrell, Mike (December 2, 2015). 'AT&T Enters Next Phase in DirecTV Branding'. MultiChannel News. Retrieved December 3, 2015.
- ^Littleton, Cynthia (April 26, 2016). 'AT&T Sees DirecTV, Broadband Subscriber Gains in Q1 as U-verse Fades'. Variety. Retrieved April 28, 2016.
- ^Hammond, Ed; Sherman, Alex; Moritz, Scott (October 20, 2016). 'AT&T Discussed Idea of Takeover in Time Warner Meetings'. Bloomberg. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^Yu, Robert (October 20, 2016). 'Report: AT&T considering buying Time Warner'. USA Today. Retrieved October 20, 2016.
- ^Hagey, Keach; Sharma, Amol; Cimilluca, Dana (October 21, 2016). 'AT&T Is in Advanced Talks to Acquire Time Warner'. The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved October 21, 2016.
- ^Yu, Roger (October 22, 2016). 'AT&T agrees to buy Time Warner for more than $80B'. USA Today. Retrieved October 22, 2016.
- ^Gryta, Thomas; Hagey, Keach; Cimilluca, Dana (October 22, 2016). 'AT&T Reaches Deal to Buy Time Warner for $86 Billion'. The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved October 22, 2016.
- ^Littleton, Cynthia (October 22, 2016). 'AT&T Sets $85.4 Billion Time Warner Deal, CEOs Talk 'Unique' Potential of Combination'. Variety. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^'Starz Accepts Rate Cut as Lionsgate Offers Stock for New Deals with AT&T'. Deadline Hollywood. September 22, 2016. Retrieved August 2, 2017.
- ^Lawler, Richard (July 13, 2017). 'AT&T's 'next-gen' TV platform rollout will start on DirecTV Now'. Engadget. Retrieved July 13, 2017.
- ^Lieberman, David (July 13, 2017). 'AT&T To Offer Cloud-Based DVR To Streaming Services'. Deadline Hollywood. Retrieved July 13, 2017.
- ^Frankel, Daniel (July 13, 2017). 'DirecTV Now to finally get cloud DVR as part of AT&T video platform rollout'. Fierce Cable. Retrieved July 13, 2017.
- ^FitzGerald, Drew; Flint, Joe (October 10, 2018). 'AT&T Streaming Video Service Is Set to Launch in 2019'. Wall Street Journal. ISSN0099-9660. Retrieved October 11, 2018.
- ^'AT&T's WarnerMedia is launching an 'HBO plus' streaming service in 2019'. The Verge. Retrieved October 11, 2018.
- ^Welch, Chris (July 9, 2019). 'WarnerMedia confirms its Netflix rival will be called HBO Max'. The Verge. Retrieved August 23, 2019.
- ^Engebretson, Joan (September 12, 2017). 'AT&T CEO: Bye-Bye DirecTV, Hello AT&T OTT Video'. Telecompetitor. Retrieved September 13, 2017.
- ^'Justice Department sues to block AT&T-Time Warner merger'. CBS News. November 20, 2017. Retrieved November 20, 2017.
- ^Fung, Brian (November 21, 2017). 'The Justice Department is suing AT&T to block its $85 billion bid for Time Warner'. The Washington Post. Retrieved November 21, 2017.
- ^'Is the AT&T merger with Time Warner being threatened because of a beef with CNN?'. TheVerge.com. November 8, 2017. Retrieved December 16, 2017.
- ^'World's 25 Biggest Telecom Companies In 2017'. Forbes. Retrieved May 25, 2017.
- ^Leichtman Research Group, 'Research Notes,' First Quarter 2012, pg. 6, AT&T (#1) with 21,232,000 residential phone lines.
- ^'AT&T Inc. Announces Filing of a Registration Statement for Potential IPO of Minority Stake in DIRECTV Latin America'. Business Wire. March 7, 2018. Retrieved March 14, 2018.
- ^Spangler, Todd (March 7, 2018). 'AT&T's DirecTV Latin America Unit Files for IPO as Prelude to Possible Spinoff'. Variety. Retrieved March 14, 2018.
- ^'AT&T Inc. Statement Regarding Planned Vrio Corp. IPO'. PR Newswire. April 18, 2018. Retrieved June 14, 2018.
- ^'At the last minute, AT&T withdraws the planned IPO of its Vrio unit'. CNBC. April 19, 2018. Retrieved June 14, 2018.
- ^Ivanova, Irina (June 12, 2018). 'Judge approves AT&T-Time Warner merger without conditions'. CBS News. Retrieved June 12, 2018.
- ^'AT&T Completes Acquisition of Time Warner Inc'. AT&T. June 15, 2018. Retrieved June 15, 2018.
- ^ ab'SEC-Show'. otp.tools.investis.com.
- ^Betz, SA Editor Brandy (September 21, 2018). 'AT&T revises segment structure on Time Warner buy'. Seeking Alpha.
- ^Bloomberg. 'AT&T Latin America LLC'. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^https://about.att.com/pages/company_profile
- ^'AT&T Completes Acquisition of Time Warner Inc'. www.businesswire.com. June 14, 2018.
- ^Spangler, Todd (June 14, 2018). 'AT&T Completes $85B Acquisition Of Time Warner'. Deadline. Retrieved November 19, 2018.
- ^Hagey, Keach; Sharma, Amol; Cimilluca, Dana (October 21, 2016). 'AT&T Is in Advanced Talks to Acquire Time Warner'. The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved October 21, 2016.
- ^Littleton, Cynthia (October 22, 2016). 'AT&T Sets $85.4 Billion Time Warner Deal, CEOs Talks 'Unique' Potential of Combination'. Variety. Retrieved October 23, 2016.
- ^'AT&T agrees to buy Time Warner for $85.4 billion'. USA TODAY. Retrieved August 8, 2017.
- ^Kang, Cecilia; Merced, Michael J. de la (November 20, 2017). 'Justice Department Sues to Block AT&T-Time Warner Merger'. The New York Times. ISSN0362-4331. Retrieved December 11, 2017.
- ^Foden, Sara; McLaughlin, David; Moritz, Scott (November 20, 2017). 'AT&T Sued by U.S. Seeking to Block Merger With Time Warner'. Bloomberg. Retrieved November 20, 2017.
- ^Littleton, Cynthia (December 22, 2017). 'AT&T, Time Warner Extend Merger Agreement Deadline as Trial Looms'. Variety. Retrieved December 22, 2017.
- ^Johnson, Ted (June 12, 2018). 'AT&T-Time Warner Merger Approved'. Variety. Retrieved June 12, 2018.
- ^'Agreements Between SNET America, Inc. (SAI) DBA AT&T Long Distance East, and AT&T Telephone Companies'. AT&T. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. Retrieved September 29, 2007.
- ^'Dan Haar column: AT&T Selling Connecticut Operations to Frontier'. tribunedigital-thecourant. Retrieved June 8, 2017.
- ^Dan Haar (October 23, 1996). 'SNET To Buy Woodbury Telephone'. The Hartford Courant. Retrieved March 9, 2018.
- ^Ausik, Paul (September 19, 2012). 'AT&T May Keep Rural Landline Business'. 24/7 Wall St. Retrieved July 22, 2013.
- ^Turmelle, Luther (October 24, 2014). 'Frontier takes over AT&T landline service Saturday'. New Haven Register. Retrieved January 7, 2016.
- ^'Corporate Inquiries.' AT&T. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^'AT&T moving headquarters to Dallas from San Antonio'. Dallas News. June 27, 2008. Archived from the original on July 4, 2008.
- ^AT&T – News Room (June 27, 2008). AT&T Corporate Headquarters to Move to Dallas. Press release. Retrieved June 27, 2008.
- ^'Corp.att.com'. Corp.att.com. Retrieved November 28, 2011.
- ^Roger Cheng, CNET. 'Done deal: AT&T closes $2.5 billion purchase of Mexico's Iusacell.' Jan 16, 2015. Retrieved Jan 4, 2018.
- ^Phil Goldstein, FierceWireless. 'AT&T closes $2.5B deal for Mexican operator Iusacell.' Jan 16, 2015. Retrieved Jan 4, 2018.
- ^Meyer, Dan (April 25, 2015). 'AT&T bolsters Mexico operations with closing of Nextel Mexico deal'. RCR Wireless News. Retrieved October 24, 2016.
- ^ abAT&T Inc. Investor Relations. 'Board of Directors'. Retrieved March 19, 2019.
- ^AT&T Inc. Investor Relations. 'Leadership'. Retrieved September 4, 2019.
- ^'Top All-Time Donors, 1989–2012'. OpenSecrets.org. United States: Center for Responsive Politics. 2018. Retrieved June 15, 2018.
- ^ abKang, Cecelia; Jia Lynn Yang (December 9, 2011). 'How AT&T fumbled its $39 billion bid to acquire T-Mobile'. The Washington Post. washingtonpost.com. Retrieved December 9, 2011.
- ^'AT&T Inc: Totals'. OpenSecrets.org. United States: Center for Responsive Politics. 2011. Retrieved December 9, 2011.
- ^Drinkard, Jim (January 17, 2005). 'Donors get good seats, great access this week'. USA Today. Retrieved May 25, 2008.
- ^'Financing the inauguration'. USA Today. January 16, 2005. Retrieved May 25, 2008.
- ^'Some question inaugural's multi-million price tag'. USA Today. Associated Press. January 14, 2005. Retrieved May 25, 2008.
- ^'Private Enterprise Board | ALEC – American Legislative Exchange Council'. Alec.org. Archived from the original on May 11, 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2012.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^May, Clifford (August 30, 1987). 'Transportation Chief Attacks Congress on Safety'. The New York Times.
- ^Goodman, Howard (March 23, 2013). 'NRA's Behind-the-Scenes Campaign Encouraged 'Stand Your Ground' Adoption'. Florida Center for Investigative Reporting.
- ^Griffin, Marshall (January 14, 2014). ''Right-to-work' bill praised and blasted in House committee hearing'. KBIA.
- ^'AT&T Inc'. The Center For Responsive Politics. Archived from the original on September 30, 2007. Retrieved September 29, 2007.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^'H.R. 3675 - CBO'. Congressional Budget Office. Retrieved March 10, 2014.
- ^Kasperowicz, Pete (March 11, 2014). 'House votes for more transparency at the FCC'. The Hill. Retrieved March 12, 2014.
- ^McKone, Tim (December 11, 2013). 'AT&T Statement on Bipartisan Spectrum and FCC Reform Legislation'. AT&T Public Policy Blog. Retrieved March 12, 2014.
- ^Bartz, Diane (May 9, 2018). 'AT&T payments to Trump lawyer more than reported'. Reuters. Retrieved May 10, 2018.
- ^Mangan, Dan; Breuninger, Kevin; Ruggiero, Ryan (May 8, 2018). 'AT&T confirms it paid Trump lawyer Michael Cohen for 'insights' on administration'. CNBC. Retrieved May 10, 2018.
- ^ abHelderman, Rosalind S.; Fung, Brian; Hamburger, Tom (May 10, 2018). 'Cohen's $600,000 deal with AT&T specified he would advise on Time Warner merger, internal company records show'. The Washington Post. ISSN0190-8286. Retrieved May 11, 2018.
- ^ abWang, Christine (May 10, 2018). 'AT&T reportedly paid Michael Cohen for guidance on Time Warner deal'. CNBC. Retrieved May 11, 2018.
- ^ abGold, Hadas (May 10, 2018). 'AT&T confirms it paid Michael Cohen for consulting on Time Warner deal'. CNNMoney. Retrieved May 11, 2018.
- ^Turner, Nick; Moritz, Scott (May 9, 2018). 'AT&T Was Paying Trump's Lawyer While White House Turned Into Foe'. Bloomberg. Retrieved May 22, 2018.
- ^Shields, Todd (May 10, 2018). ''No' Cohen Inquiries on Net Neutrality on AT&T's Behalf, FCC Chairman Says'. Bloomberg. Retrieved May 22, 2018.
- ^Thomas, Katie; Kang, Cecilia (May 9, 2018). 'Novartis and AT&T Spoke to Mueller's Office About Payments to Michael Cohen'. The New York Times. ISSN0362-4331. Retrieved May 10, 2018.
- ^Mangan, Dan; Ruggiero, Ryan (May 9, 2018). 'AT&T says it was contacted by special counsel's office about Michael Cohen'. CNBC. Retrieved May 10, 2018.
- ^Cristiano Lima (April 16, 2019). 'White House denies House Democrats' AT&T-Time Warner records request'. Politico.com. Retrieved April 16, 2019.
- ^'Annual Report 2015'. AT&T Inc. Retrieved June 8, 2016.
- ^'Annual Report - 2014'(PDF). AT&T Inc. Retrieved November 17, 2015.
- ^'SEC Filings — Form K-10 - 2005'. AT&T Inc. March 1, 2006. Retrieved November 18, 2015.
- ^'Annual Report 2016'. AT&T. February 17, 2017. Retrieved February 21, 2017.
- ^Fisher, Ken (October 1, 2007). 'AT&T threatens to disconnect subscribers who criticize the company'. Arstechnica.com. Retrieved November 28, 2011.
- ^'AT&T Legal Policy'. AT&T. Archived from the original on October 11, 2007. Retrieved September 29, 2007.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^Martin H. Bosworth. 'AT&T Changes Terms Of Service After Outcry'. Consumeraffairs.com. Archived from the original on January 2, 2012. Retrieved November 28, 2011.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^'AT&T Legal Policy'. Att.net. May 2, 2011. Retrieved November 28, 2011.
- ^'Klein Exhibit' Document from Hepting vs AT&T lawsuit from 2007. Reported by Ryan Singel in Wired Magazine, article 'AT&T 'Spy Room' Documents Unsealed; You've Already Seen Them' June 13, 2007, Documents posted at the Electronic Frontier Foundation website: (File 'SER_klein_exhibits.pdf')
- ^Nakashima, Ellen, 'A Story of Surveillance', Washington Post, November 7, 2007
- ^Singel, Ryan (April 7, 2006). 'Whistle-Blower Outs NSA Spy Room'. Wired. Retrieved September 29, 2007.
- ^'Government Moves to Intervene in AT&T Surveillance Case' (Press release). Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF). April 28, 2006. Archived from the original on September 29, 2007. Retrieved September 29, 2007.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^Arshad Mohammed, Washington Post. 'Judge Declines to Dismiss Lawsuit Against AT&T.' Jul 21, 2006. Retrieved Jan 4, 2018.
- ^Cauley, Leslie (May 11, 2006). 'NSA has massive database of Americans' phone calls'. USA Today. Retrieved September 29, 2007.
- ^Lazarus, David (June 21, 2006). 'AT&T Rewrites Rules: Your Data Isn't Yours'. San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on November 12, 2007. Retrieved September 29, 2007.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^Shrader, Katherine (August 22, 2007). 'Spy Chief Reveals Classified Surveillance Details'. Associated Press. Archived from the original on September 13, 2007. Retrieved September 29, 2007.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^Olbermann, Keith (November 8, 2007). 'Whistleblower Saw AT&T Assist Bush Administration'. MSNBC. Archived from the original on November 10, 2007. Retrieved November 10, 2007.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^Svensson, Peter (September 29, 2011). 'Document Shows How Phone Cos. Treat Private Data'. Retrieved May 13, 2019.
T-Mobile USA doesn't keep any information on Web browsing activity. Verizon, on the other hand, keeps some information for up to a year that can be used to ascertain if a particular phone visited a particular Web site. According to the sheet, Sprint Nextel Corp.'s Virgin Mobile brand keeps the text content of text messages for three months. Verizon keeps it for three to five days. None of the other carriers keep texts at all, but they keep records of who texted who for more than a year. The document says AT&T keeps for five to seven years a record of who text messages who —and when, but not the content of the messages. Virgin Mobile only keeps that data for two to three months.
- ^'Who Has Your Back? Government Data Requests 2017'. July 10, 2017.
- ^ abWu, Tim (January 16, 2008). 'Has AT&T Lost Its Mind? A baffling proposal to filter the Internet'. Slate.
- ^'AT&T's Proposed Filtering Policy Is Bad News – Netiquette – MSNBC.com'. MSNBC. January 25, 2008. Retrieved November 28, 2011.
- ^ abcd(March 9, 2009) 'AT&T Accused of Discriminating Against Local Public Access Channels, Deadline for Public Comment Expires Tonight', Democracy Now!. Retrieved March 13, 2009.
- ^ abcdKeizer, Gregg (June 10, 2010). ''Brute force' script snatched iPad e-mail addresses'. Computerworld. Retrieved September 18, 2010.
- ^Keizer, Gregg (June 11, 2010). 'iPad e-mail hackers defend attack as 'ethical''. Computerworld. p. 2. Retrieved September 25, 2010.
- ^ abKeizer, Gregg (June 11, 2010). 'iPad e-mail hackers defend attack as 'ethical''. Computerworld. p. 1. Retrieved September 25, 2010.
- ^'AT&T pays record $25m fine over customer data thefts'. April 9, 2015.
- ^'F.C.C. Fines AT&T $25 Million for Privacy Breach'. New York Times. April 8, 2015.
- ^'Welcome to the United States Department of Justice'. Justice.gov. March 22, 2012. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ^ABC News. 'Technology and Science News — ABC News'. ABC News.
- ^'Aaron Slator, AT&T president, fired over racist text messages'. The Washingtion Times.
- ^'Protesters Picket AT&T CEO's Dallas Estate'. CNN iReport.
- ^'Citigroup trademarks 'THANKYOU' and sues AT&T for thanking clients'. Ars Technica. Retrieved June 16, 2016.
- ^'Citigroup Sues AT&T Over Right to Say 'Thanks' to Customers'. Bloomberg. Retrieved June 17, 2016.
- ^'AT&T beats Citi challenge over saying 'thanks' to customers'. The New York Post. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- ^'Teamusa.org'. Teamusa.org. Archived from the original on December 5, 2011. Retrieved November 28, 2011.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^'NCAA.org'. NCAA.org. December 14, 2007. Archived from the original on September 29, 2011. Retrieved November 28, 2011.Cite uses deprecated parameter
|deadurl=(help) - ^'AT&T and Infiniti Red Bull Racing – Speeding up Team Communications'. AT&T Newsroom. AT&T. Retrieved May 27, 2016.
- ^'AT&T Taking Esports Strategy to New Heights with Cloud9 Agreement'. AT&T. March 5, 2019. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
- ^Fitch, Adam (March 5, 2019). 'Cloud9 enters sponsorship deal with AT&T'. Esports Insider. Retrieved March 26, 2019.
External links[edit]
At&t Pc Maintenance
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to AT&T. |
- Corporate information
Mac System Tools
- Business data for AT&T:
- AT&T History and science resources at The Franklin Institute's Case Files online exhibit




